Customer Relationship Management has become the backbone of modern business operations, evolving from simple contact databases to sophisticated AI-driven systems that can autonomously manage complex customer interactions. As businesses navigate an increasingly competitive landscape, understanding the spectrum of CRM technologies—from traditional systems to cutting-edge agentic platforms—has become essential for sustainable growth.
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) represents the combination of strategies, technologies, and practices that organizations use to manage and analyze customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle. The primary objective is to improve customer service relationships, assist in customer retention, and drive sales growth by maintaining a comprehensive, accessible record of every customer touchpoint.
Modern CRM systems serve as centralized platforms where businesses consolidate customer data from multiple channels including email, phone, social media, websites, and in-person interactions. This consolidation breaks down organizational silos, ensuring that every department—from sales and marketing to customer service—operates with the same comprehensive understanding of each customer.
The core components of CRM include contact management for maintaining detailed customer profiles and interaction histories, sales management for tracking deals through the pipeline, marketing automation for targeted campaigns and lead nurturing, customer service tools for managing support tickets and ensuring timely resolution, and analytics capabilities that transform raw data into actionable insights. These systems also incorporate workflow automation to eliminate repetitive tasks and maintain consistency in customer interactions, while collaboration tools ensure teams can work together effectively on customer accounts.
The benefits of implementing CRM extend throughout the organization. Sales teams experience improved lead conversion rates and shorter sales cycles, marketing departments achieve better campaign ROI through targeted segmentation, and customer service teams resolve issues faster with complete customer context. From an organizational perspective, CRM provides improved forecasting accuracy, better customer retention rates, and data-driven decision making capabilities that drive strategic growth.
Traditional CRM Systems and Market Leaders
The CRM market has matured significantly over the past two decades, with several platforms emerging as industry leaders. Salesforce, the undisputed market leader, offers a comprehensive cloud-based platform that serves businesses from startups to Fortune 500 companies. Its extensive ecosystem of applications and integrations through the AppExchange marketplace makes it highly customizable for various industry needs.
HubSpot CRM has gained significant traction, particularly among small to medium-sized businesses, by offering a robust free tier and an intuitive interface that reduces the learning curve typically associated with CRM adoption. The platform’s strength lies in its seamless integration between marketing, sales, and service hubs, providing a unified customer experience platform.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 leverages deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, making it particularly attractive for organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies. The platform combines CRM and ERP capabilities, offering a comprehensive business application suite that extends beyond traditional customer relationship management.
Pipedrive focuses specifically on sales teams, providing a visual pipeline management system that makes it easy to track deals and activities. Its simplicity and sales-centric design have made it popular among sales-driven organizations that prioritize ease of use over extensive features. Meanwhile, Zoho CRM offers an affordable yet feature-rich solution that includes AI capabilities through Zia, making advanced CRM accessible to smaller businesses with limited budgets.
The Evolution to AI-Powered CRM
Artificial Intelligence has fundamentally transformed CRM capabilities, shifting these platforms from reactive data repositories to proactive, intelligent systems that anticipate customer needs and automate complex decision-making processes. AI-powered CRM leverages machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to uncover patterns and insights that would be impossible for humans to identify manually.
The integration of AI into CRM manifests through several key capabilities. Predictive lead scoring uses historical data and behavioral patterns to automatically rank leads by conversion probability, continuously refining its accuracy through machine learning. This enables sales teams to focus their efforts on the most promising opportunities. Sentiment analysis powered by natural language processing examines customer communications across all channels, identifying emotional undertones and potential issues before they escalate into problems.
Salesforce Einstein represents one of the most comprehensive AI CRM implementations, offering predictive scoring, automated data capture, and intelligent recommendations across sales, service, and marketing. Einstein continuously learns from your data, becoming more accurate and valuable over time. It can predict which deals are most likely to close, recommend next best actions for sales reps, and automatically route cases to the right service agents.
Freshsales incorporates Freddy AI to provide intelligent sales insights, including contact scoring, deal insights, and automated workflows. The system analyzes sales activities to identify successful patterns and coaches representatives on optimal engagement strategies. Similarly, Zoho’s Zia AI assistant can predict the best time to contact customers, detect anomalies in sales patterns, and even suggest the most effective email subject lines based on historical performance data.
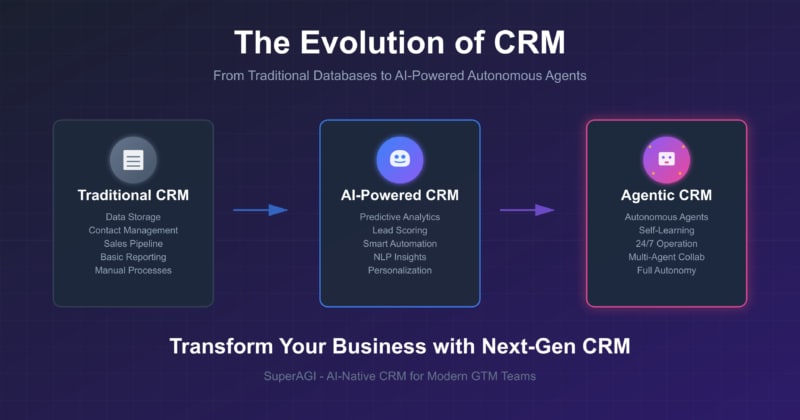
SuperAGI: Pioneering AI-Native CRM for Modern GTM Teams
SuperAGI represents a new generation of AI-native CRM platforms that fully embrace autonomous agent technology from the ground up. Unlike traditional CRM systems that add AI features as enhancements, SuperAGI is built entirely around AI agents that work together to drive predictable revenue growth. The platform positions itself as the best AI sales platform in the world, offering a comprehensive suite of tools designed for unified sales, marketing, and support operations.
What sets SuperAGI apart is its focus on AI GTM (Go-To-Market) agents that can autonomously handle complex sales and marketing workflows. The platform’s AI Outbound and Inbound SDRs (Sales Development Representatives) work around the clock to identify, qualify, and engage prospects without human intervention. These AI SDRs can research companies, personalize outreach at scale, handle objections, and book meetings directly into sales reps’ calendars. The system learns from every interaction, continuously improving its engagement strategies and conversion rates.
SuperAGI’s AI Journey feature creates intelligent, multi-touch customer journeys that adapt in real-time based on prospect behavior and engagement patterns. Rather than following rigid sequences, the platform’s agents dynamically adjust messaging, timing, and channels to maximize engagement. The AI Dialer enables intelligent voice conversations, with AI agents capable of conducting initial qualification calls and seamlessly transferring warm leads to human sales representatives when appropriate.
The platform’s Signals capability monitors buying intent across multiple data sources, alerting sales teams to opportunities in real-time. This includes tracking website visits, content engagement, competitive research activities, and social signals that indicate purchase readiness. When combined with the Agent Builder feature, businesses can create custom AI agents tailored to their specific industry, sales process, and customer base without requiring technical expertise.
SuperAGI’s approach to CRM goes beyond traditional record-keeping to active revenue generation. The Revenue Analytics component provides predictive insights into pipeline health, forecast accuracy, and revenue opportunities, while the Journey Orchestration feature ensures consistent, personalized experiences across all touchpoints. The platform’s Customer Data Platform unifies data from multiple sources, creating comprehensive customer profiles that inform every interaction.
The Omnichannel Marketing capabilities enable coordinated campaigns across email, social media, SMS, and other channels, with AI agents optimizing message delivery and content based on individual preferences and behaviors. The Segmentation engine uses machine learning to identify micro-segments and personalize engagement strategies for each group, moving beyond basic demographic or firmographic targeting to behavioral and intent-based segmentation.
For organizations looking to implement truly autonomous sales and marketing operations, SuperAGI offers a compelling vision of what AI-native CRM can achieve. The platform’s focus on GTM agents addresses the primary challenge facing modern sales teams: the need to do more with less while maintaining personalization at scale.
The Emergence of Agentic CRM
Agentic CRM represents the next evolutionary leap in customer relationship management, introducing autonomous AI agents that can independently execute complex tasks, make decisions, and manage entire customer interaction workflows without constant human oversight. Unlike traditional AI that primarily provides insights and recommendations, agentic systems actively participate in customer relationship management, operating as digital team members with specific roles and responsibilities.
These systems deploy specialized agents across the customer lifecycle. Prospecting agents autonomously identify potential customers by analyzing vast data sources, understanding buying signals, and conducting initial outreach. They can research companies, identify decision-makers, personalize messaging, and maintain persistent follow-up campaigns. Meeting agents handle the complex logistics of scheduling, send personalized preparation materials, and can even conduct certain types of meetings autonomously, ensuring all participants have relevant context and capturing action items for follow-up.
Support agents have evolved far beyond simple chatbots, providing sophisticated customer service by understanding complex, multi-faceted issues, accessing multiple backend systems to resolve problems, and knowing precisely when human intervention is necessary. These agents can handle everything from routine password resets to complex technical troubleshooting, learning from each interaction to improve future performance.
Campaign agents autonomously design, execute, and optimize marketing campaigns, adjusting messages, timing, and channels based on real-time performance data. They can run multivariate tests, identify winning combinations, and automatically scale successful strategies. Territory and operations agents optimize sales coverage by analyzing performance data, market potential, and rep capacity to automatically redistribute leads and accounts for maximum efficiency.
The multi-agent framework in agentic CRM enables these specialized agents to collaborate, sharing information and coordinating activities to achieve complex business objectives. For example, when a prospecting agent identifies a high-value opportunity, it can automatically engage the meeting agent to schedule a demo, notify the relevant sales rep, and trigger the campaign agent to begin a targeted nurture sequence—all without human intervention.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
The practical applications of modern CRM systems span across industries and business functions, delivering tangible results that directly impact revenue and customer satisfaction. In sales automation, AI-powered and agentic CRM systems have transformed how organizations identify, qualify, and convert leads. For instance, a software company implementing agentic prospecting agents reported a 40% increase in qualified pipeline within three months, as the agents worked 24/7 to identify and engage potential customers across multiple channels.
Customer service departments leverage AI CRM to predict and prevent issues before they escalate. A telecommunications company using predictive analytics identified customers likely to experience service disruptions and proactively reached out with solutions, reducing support ticket volume by 30% and improving customer satisfaction scores significantly. The support agents could handle routine inquiries autonomously, allowing human agents to focus on complex, high-value interactions that require empathy and creative problem-solving.
Marketing teams use AI-powered personalization to deliver highly targeted campaigns that resonate with individual customers. An e-commerce retailer implementing AI-driven product recommendations and personalized email campaigns saw a 25% increase in average order value and a 35% improvement in email engagement rates. The system continuously learned from customer interactions, refining its personalization algorithms to become more effective over time.
In the B2B space, agentic CRM systems have revolutionized account-based marketing and sales strategies. A technology services company deployed a multi-agent system that coordinated prospecting, nurturing, and engagement activities across their enterprise accounts. The prospecting agents identified expansion opportunities within existing accounts, meeting agents scheduled quarterly business reviews, and campaign agents delivered personalized content based on each stakeholder’s role and interests. This coordinated approach resulted in a 50% increase in account expansion revenue.
Top CRM Tools and Platforms to Consider
When evaluating CRM solutions, organizations should consider both established platforms with AI capabilities and emerging agentic solutions. HubSpot’s AI-powered CRM offers predictive lead scoring, conversation intelligence, and content optimization tools that make sophisticated AI accessible to businesses of all sizes. Their ChatSpot AI assistant can help users interact with their CRM using natural language, making data retrieval and task execution more intuitive.
Monday.com CRM provides a highly customizable platform with AI-powered automation capabilities that can adapt to various business processes. Its visual interface and flexible structure make it particularly suitable for teams that need to manage complex, multi-stage customer journeys. Insightly combines CRM with project management capabilities, using AI to provide relationship insights and predict project outcomes based on historical data.
For organizations specifically interested in agentic capabilities, platforms like Clay offer advanced data enrichment and automated outreach capabilities that border on autonomous operation. These platforms can automatically research prospects, enrich contact data from multiple sources, and execute personalized outreach campaigns with minimal human intervention.
Apollo.io provides a comprehensive sales intelligence and engagement platform that combines a vast B2B database with AI-powered sequencing and automation tools. The platform can identify ideal customer profiles, automatically build targeted lists, and execute multi-channel outreach campaigns while continuously optimizing based on performance data.
Enterprise organizations should also consider Oracle CX Cloud, which offers sophisticated AI capabilities through its Adaptive Intelligent Apps, providing predictive insights and recommendations across sales, marketing, and service functions. The platform’s strength lies in its ability to handle complex, high-volume enterprise requirements while maintaining performance and security standards.
Implementation Best Practices
Successfully implementing modern CRM requires careful planning and a structured approach that addresses both technical and organizational challenges. Data preparation forms the foundation of any successful CRM implementation. Organizations must audit existing data sources, establish data quality standards, and create a comprehensive data migration strategy. This includes identifying and resolving duplicate records, standardizing data formats, and enriching incomplete records before migration.
Integration architecture requires careful consideration, particularly for AI and agentic systems that need to access multiple data sources and systems. Organizations should map all customer touchpoints and ensure the CRM can integrate with existing tools including marketing automation platforms, customer support systems, accounting software, and communication tools. APIs and integration platforms like Zapier or Workato can facilitate these connections, enabling seamless data flow across the technology stack.
Change management often determines the success or failure of CRM implementations. Organizations should develop a comprehensive training program that addresses different user roles and skill levels. Start with a pilot program involving enthusiastic early adopters who can become internal champions. Their success stories and feedback can help refine the implementation before broader rollout. Establish clear metrics for success, including adoption rates, data quality scores, and business impact measurements.
For AI and agentic CRM implementations, organizations must establish governance frameworks that define autonomy levels, decision boundaries, and escalation protocols. Create clear guidelines for when human intervention is required and ensure there are mechanisms for humans to override agent decisions when necessary. Implement feedback loops that allow agents to learn from human corrections and continuously improve their performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing advanced CRM systems presents several challenges that organizations must address proactively. Data privacy and security concerns have intensified with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, requiring organizations to implement robust data governance practices. CRM systems must include features for consent management, data retention policies, and the ability to fulfill data subject requests. Organizations should conduct regular security audits and ensure their CRM vendors maintain appropriate certifications and compliance standards.
The human-AI collaboration dynamic requires careful management to ensure technology augments rather than replaces human capabilities. Employees may resist adoption due to fears of job displacement or skepticism about AI accuracy. Address these concerns through transparent communication about how AI will support their work, comprehensive training programs that build confidence, and involving users in the implementation process to ensure the system meets their actual needs.
Data quality remains a persistent challenge, as AI and agentic systems are only as effective as the data they process. Organizations must implement data governance policies that ensure consistent data entry, regular data cleansing, and ongoing enrichment. Establish data stewardship roles and use automated data quality tools to identify and resolve issues before they impact system performance.
The Future of CRM Technology
The future of CRM technology points toward increasingly sophisticated autonomous systems that can manage entire customer relationships with minimal human intervention. Generative AI and large language models are already beginning to transform how CRM systems understand and respond to customer needs. These technologies will enable more natural conversations, better understanding of context and intent, and the ability to generate personalized content at scale.
Platforms like SuperAGI are leading this transformation by demonstrating what’s possible when AI agents are given the autonomy to manage complete go-to-market workflows. As these systems mature, we’ll see the emergence of fully autonomous sales teams where AI agents handle everything from initial prospecting to contract negotiation, with humans focusing on strategic decision-making and complex relationship management.
The convergence of CRM with other business systems will accelerate, creating unified platforms that manage the entire customer journey from marketing to sales to service to success. These platforms will break down the artificial boundaries between departments, enabling truly customer-centric organizations. Integration with IoT devices and edge computing will provide real-time customer data that enables immediate response to customer needs and behaviors.
The democratization of advanced CRM capabilities will continue, making sophisticated AI and automation accessible to smaller businesses. No-code and low-code platforms will enable business users to create and deploy custom agents without technical expertise. This will level the playing field, allowing smaller organizations to compete with enterprises in terms of customer experience and operational efficiency.
As CRM technology evolves, the focus will shift from managing customer data to orchestrating customer experiences. The most successful organizations will be those that effectively blend human creativity and empathy with AI efficiency and scale. While technology will handle routine tasks and data analysis, humans will focus on strategic thinking, relationship building, and handling complex situations that require emotional intelligence and creative problem-solving.
The journey from traditional CRM to AI-powered and agentic systems represents a fundamental shift in how businesses think about and manage customer relationships. Organizations that embrace these technologies while maintaining a human-centric approach will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and customer-driven marketplace. The key is not to view these systems as replacements for human interaction, but as powerful tools that enable businesses to deliver more personalized, efficient, and meaningful customer experiences at scale.






